UPDATE 2 (2014-5-7): The exact legal status of some of the ports remains a mystery. I have attempted to clarify and point out some of the remaining areas of confusion below.
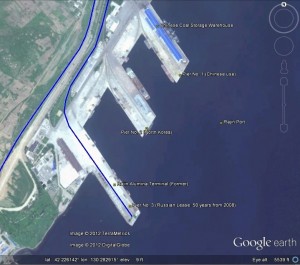
Pictured above (Google Earth): A 2013-9-14 satellite image of Rason Piers 1 and 2. Pier 1 (Top) is used by the Chinese. The Royale Star is docked at Pier 2.
When Jang Song-thaek was purged, among the laundry list of offenses he was alleged to have committed against the regime was this:
Jang made no scruple of committing such act of treachery in May last as selling off the land of the Rason economic and trade zone to a foreign country for a period of five decades under the pretext of paying those debts.
This phrase had Pyongyang watchers abuzz over whether Chinese contracts in Rason were in any danger of being violated by the North Korean government. Of course it was immediately unclear what enterprise(s) would be affected since we are all unaware of any significant deals reached in May of 2013.
A recent statement by a North Korean official in the Hong Kong media has, however, raised the issue of contract credibility in the DPRK yet again.
According to Yonhap:
Chinese companies have not leased piers at a port of North Korea’s free trade zone, a Pyongyang official has told Hong Kong media, raising speculation that the shock execution of the North Korean leader’s uncle might have soured business ties with its key ally.
China reportedly agreed to invest about US$3 billion in developing the free trade zone in North Korea’s northern tip of Rason, formerly known as Rajin and Sonbong, in late 2011. The special trade zone sits across the border from China’s northeastern Jilin province.
There have been media reports that Chinese companies have leased two piers at the Rason port, but Kim Chun-il, a division chief of the port’s foreign business bureau, denied such reports during an interview with Hong Kong-based Phoenix TV.
Asked by a Phoenix TV journalist whether China won the right to exclusively use two piers at the port, Kim replied in Korean, “There are no piers that are specially used by the Chinese side.”
“They (Chinese people) have said so, but we have never formally rented out Pier 1 and Pier 2 to them,” Kim said.
The interview was made during a 72-minute special TV program on the Rason trade zone, which was aired on April 19. The program’s video footage can be seen on the website of Phoenix TV.
Kim said that Russia leased the Pier 3 at the port, adding that North Korea plans to modernize the two piers on its own.
The Chinese media did indeed claim at least once (see here) that they were “using” Piers 1 and 2. And Dr. Bernhard Seliger told us back in September 2012 that the Chinese were using the port, although no lease was signed [see below].
However, it is not true that the North Koreans have never announced an agreement on Pier 1 at Rason. I posted an article (back in March of this year) in which Choe Hyon Chol, section chief of the new State economic Development Commission, stated the following:
The Rajin Port, a transit trade port, is the hub of international cargo transit transportation and transport of exports and imports of entrepreneurs who invested in the zone.
The port has assignments to transport marine products for export from the East Sea of Korea and every kind of cargoes from and to northeast area of China and Far East Region of Russia.
The Rajin Port consists of three wharves; wharf No. 1 is designed to be renovated and operated by China Dalian Chuang Li Co., Ltd. and wharf No.3 by Rason International Container Transport J. V. Company to be set up according to the contract with Russian Rail Trade Co., Ltd.
I cannot imagine that a Chinese company is going to renovate and operate the pier without a clear contract. Of course the status of that contract is now called into question. Has the Chinese firm pulled out? Have the North Koreans canceled the contract? Are North Korean individuals from different agencies just not on the same page? Who knows?
Still no word on Pier No. 2.
Great recent photos of Rason port by Ray Cunningham here.
You can read the Yonhap story here:
N. Korean official says no piers for China at special trade zone
Yonhap
2014-5-2
UPDATE 1 (2012-9-5): It appears the information in the original post is out-of-date now. So here is an update:
Pictured Above (Google Earth): Rajin Port
Dr. Bernhard Seliger of the Hanns Seidel Foundation writes in with an update on the Rajin Port:
The 80 year old port has three piers, of which the No. 3 pier is used by the Russians. They have a long-term lease (50 years starting in 2008) and while they are currently doing some work there, it is not being used for exports.
China is interested in using Pier No.1 (where it rents a warehouse to store coal) and Pier No. 2 (currently in use by the Koreans). Plans have also been expressed (now cancelled) to build 2 new piers (No. 4 and 5) (See here). For many years the Chinese and North Korean governments have negotiated a pier rental agreement, but for now there is no concrete result–though at numerous times it has been maintained that China already rented the port. What exactly the problems are is not known. For now China uses the port to bring coal from the northernmost Heilongang Province to southern China via a sea route, an event which took place twice this year.
Theoretically, the port as a handling capacity of 3 million sq. tons, however the maximum real handling was 800.000 tons in 1979, while last year it was 200.000 tons. The depth of the harbor is 9 m.
In a report from Xinhua (2012-8-28), the Chinese assert they are using ports 1 and 2.
China […] was using No. 1 and 2 piers, while Russia had leased No. 3 pier, said an official in charge of foreign affairs of the port.
So there is some discrepancy between the Chinese account and Dr. Seliger.
ORIGINAL POST (2010-5-23): What are the three piers at Rason used for?
The City of Rajin (Rason) has three ports (pictured above–click for large version). According to a 1998 UNDP report, Pier No. 1 (on the right) was known as the “Russian-Japanese Bulk Fertilizer Terminal. It has now been leased by the Chinese. Port No. 3 (left) was formerly known as the Rajin Alumina Terminal. This is now leased by the Russians (see here). A fellow North Korea-watcher tells me that Pier No. 2 is reserved for the North Koreans.
KBS recently ran a video on recent changes in Rason. I have uploaded the segment to YouTube (Apologies to readers in China). You can see the video here.
On a side note, if anyone in China has the time and savvy to rip videos from my YouTube account and re-post them on Youku please go for it.