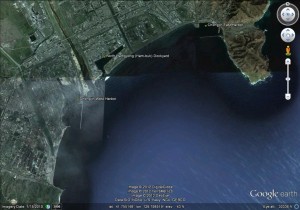
Pictured Above: The Orang Odaejin Fisheries Office
According to the Daily NK:
Daily NK has learned that approximately 30 North Korean squid fishing vessels from ports in the provinces of North and South Hamkyung have been lost at sea this year alone, causing more than 120 casualties.
A source from North Hamkyung Province revealed the news to Daily NK on the 18th, explaining that the information came from the ‘2012 Missing Vessels Report,’ a booklet of statistical data compiled by the regional coast guard.
According to the source, the report noted, “Among all the vessels that have engaged in squid fishing this year, more than 30 smaller vessels have been lost, and 122 crew members have been killed or reported missing.”
It is mandatory for fishing vessels to register a crew list before leaving port each day for security reasons. Those vessels that leave port but do not return are classified as lost.
The sea near the Hamkyung port of Odaejin in Eorang County has traditionally been the most popular on the North Korean East Sea coast for squid fishing. However, Jang Keum Chun, who previously operated a shipping company in the Liaoning Province city of Dalian, has had a number of boats in the area since 2007.
This is because Jang is the son of Jang Wool Hwa, who sided with Kim Il Sung during the fight for liberation from Japanese rule. As such, he is said to have received direct permission from Kim Jong Il to begin fishing in the area.
The local fishermen who had been fishing for squid in the region for generations have been progressively forced further and further out by this (plus declining squid stocks throughout the East Sea region), which has put many in grave danger.
The source said, “North Korean fishing vessels only have about 6 to 8Hp, so are easily swayed by strong winds and waves.” When vessels run into trouble, there is little hope of rescue due to inadequate communications equipment and rescue vessels.
North Korea has reportedly been suffering 100 or more casualties in fishing accidents in the region for a number of years.
Read the full story here:
122 Casualties in Race for Squid
Daily NK
Choi Song Min
2012-12-18