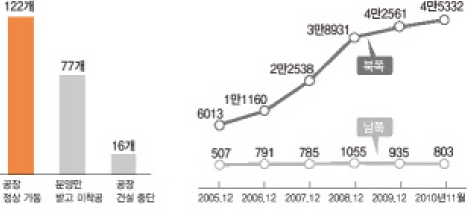
Image from the Hankyoreh: The left graph shows the number of South Korean tenant companies operating at Kaesong Industrial Complex. 122 companies are operating normally, 77 companies are not currently operating, and 16 have halted operations. The right graph shows the total number of workers: above, the number of North Korean workers and below, the number of South Korean workers.
According to the Hankyoreh:
… [Companies in the Kaesong Zone] complained that they have lost hundreds of millions of Won (hundreds of thousands of dollars) with the suspension of factory construction due to administration measures forbidding new investment. They also said that the situation is growing bleaker by the day, with veteran employees quitting as the numbers of resident personnel at the complex drops due to concerns about personal safety. Despite all of this, they suffer without a word of formal complaint out of fears that they might draw the anger of North Korean and South Korean authorities.
In its May 24 measures last year, the Lee administration declared a suspension to trade and exchanges with North Korea in response to the sinking of the Cheonan. At the complex, only existing facilities were allowed to operate, while the resident workforce was halved to 500 people and the introduction of additional equipment was prohibited. Sixteen companies that were in the process of building new factories suffered a direct hit from these measures. At present, a total of 122 small and medium companies run factories in the complex.
Company “A,” a garment company that invested 5 million Won ($4,493) in inter-Korean economic cooperation funding to build a sewing factory, but were forced to suspended construction with approximately 90 percent of the process complete.
“Only the exterior and interior remain,” said the president of the company. “We could not bring in factory equipment, so we just gave up.”
The Export-Import Bank of Korea (EXIM) only stood surety for 90 percent of the loan, so Company A faces the immediate burden of principal and interest repayments in the hundreds of millions of Won. It also has to pay 16 million Won per year in interest on the EXIM-guaranteed loan until compensation money comes from the government.
The company’s president said, “We borrowed the money because they said to do an inter-Korean economic cooperation project, and then they just cause a loss by suspending exchange. Is the administration playing interest games with South Koreans?”
To date, a total of 1.26 trillion Won ($1.1 billion) has been invested in the complex, the bulk of which is facility investment paid by tenant companies, amounting to 730 billion Won.
Company “B,” another garment company, originally had seven South Korean employees working with 330 North Korean workers. But following the order from Seoul to halve the number of resident employees, there are now just three South Korean employees left. Two employees left the company. “The employees who left were heads of household in their forties who had worked with us for over a decade,” the president sighed. “They had a difficult time getting up at 6 in the morning for the 70 to 80 kilometer commute, and the government actually ended up fanning anxieties with its talk about ‘protecting employee safety,’ so their family members dissuaded them from working at the complex.”
Hiring new employees is not an option. In some cases, interviews were held and start dates were set before the new recruits abandoned their plans after the Yeonpyeong Island shelling occurred two months ago. Company B, which has its head office in Seoul, is in a slightly better position. Employees at businesses in Daegu, Gwangju, and Busan, for whom commuting is impossible, are forced to stay at motels in Munsan, Gyeonggi Province.
“They emptied out a perfectly good dormitory in the Kaesong complex, and employees have been wasting time, money, and strength for months now,” said the president of Company “C.” “It stands to reason that the departure rate is increasing.”
The president of Company “D” stated emphatically that there is no physical risk at the complex. In fact, the president said, North Korean authorities have added more productive labor on site since the Cheonan sinking and the bombardment of Yeonpyeong Island. The 45,332 North Korean workers as of November 2010 represented an increase of a full 2,771 over the 42,561 working in 2009. The president of Company D stressed that the government must increase the number of resident personnel if the physical safety of South Korean employees is to be guarded.
“If it is impossible to guarantee physical safety, they should not be leaving a single person at the Kaesong complex,” the president said. “Does it make any sense to say that 500 people is okay, but 1,000 is not?”
Some buyers have also fallen away because of anxieties. In late 2010, garment company “E” lost a buyer that had previously been purchasing 70 percent of its production output. “They got worried when it became difficult to bring in raw materials due to the sanctions against North Korea, and finally they halted transactions, saying that they thought the government had washed its hands of the Kaesong complex,” the president of Company E said. “Even if we suspend operations because there is no work to do, we still have to pay the workers’ wages, so the deficit is increasing by the day.”
With the decreased South Korean presence, six commercial facilities within the complex have also closed down, including a supermarket, restaurant, and singing room at “Songak Plaza.”
“If you look at the Gaeseong Industrial Complex Support Act, which the National Assembly passed unanimously, the government is to provide support and guarantees so that we can conduct business freely, like companies do in any other region,” said the president of Company F. “We are on the brink of withering away because of this idea of restricting property rights and company activities for administrative expedience, and through a minister’s order rather than any law.”
While they have been driven to the brink, the company presidents are adamantly opposed to closure of the complex. The president of Company G explained, “At first, things were rocky because of cultural and ideological differences, but now the North Korean workers understand the companies. They have realized by themselves why we need to meet the delivery deadline, why we need to improve quality, why we need to make so much. The Kaesong complex is performing the role of reducing the costs of reunification by restoring homogeneity between North Korea and South Korea.”
The president of Company H said, “The possibility of war is also being checked by the presence of North Korean and South Korean workers in the complex.”
“For the sake of peace and shared prosperity, we need to develop [the complex] into a special economic zone of peace where North Korea and South Korea can communicate,” the president added.
According to the Choson Ilbo:
Six of nine commercial [leisure] facilities in the joint Korean Kaesong Industrial Complex have closed, it emerged on Tuesday.
According to the Unification Ministry, a supermarket, a beer hall, a karaoke and a billiard hall in the Songak Plaza, the industrial park hotel operated by Hyundai Asan, closed on Dec. 1, right after North Korea’s shelling of Yeonpyeong Island. Already in February a massage parlor closed, and in August a Japanese restaurant.
Only a duty-free shop and Korean and Chinese restaurants managed directly by Hyundai Asan stay open. A staffer at the industrial park said the reason is that the number of South Korean staffers in the industrial park, who were the main customers of the facilities, has dropped sharply.
There were some 1,200 to 1,500 South Koreans at the industrial park until the North’s sinking of the Navy corvette Cheonan in March and its shelling of Yeonpyeong in November, but the number dropped to about 500 recently.
According to Yonhap:
Production at an inter-Korean industrial park dropped 15 percent in November last year when the North bombarded a South Korean island, raising bilateral tensions to the highest level in years, the Unification Ministry said Sunday.
The fall, however, contrasted with an increase in the number of North Korean workers at the Kaesong industrial park, located just north of the heavily armed inter-Korean border, the ministry said on its Web site.
Over 45,000 North Koreans were working as of November for more than 120 South Korean firms at the complex, the ministry said, adding that they produced US$25.1 million worth of products that month, compared to $29.4 million in October.
The factory park is considered the last remaining symbol of reconciliation between the two Koreas that remain divided by a heavily armed border after the Korean War ended in a truce in 1953.
After North Korea shelled the western South Korean island of Yeonpyeong on Nov. 23, killing four people, Seoul restricted the number of South Korean workers allowed to stay overnight in Kaesong.
The measure, which remains in place, led business managers to complain of difficulties in production. South Korea maintains it will continue to support manufacturing activities at the Kaesong industrial park despite the North Korean provocation.
Since May when a multinational investigation led by Seoul found the North responsible for the sinking of a South Korean warship earlier that year, South Korea has suspended all cross-border trade with North Korea.
Read the full stories here:
Kaesong companies on the brink as sanctions continue
Hankyoreh
Jung Eun-joo
1/19/2011
Leisure Facilities at Kaesong Close Down
Choson Ilbo
1/19/2011
Output at inter-Korean factory park falls amid tension
Yonhap
1/23/2011

