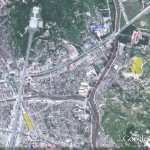
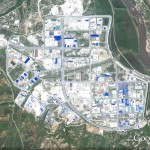
UPDATE 1 (2011-8-10): Wages of North Korean workers in Kaesong Industrial Complex set to rise 5% for the fifth consecutive year. According to the Institute for Far Easter Studies (IFES):
The minimum wage for North Korean workers at the Kaesong Industrial Complex (KIC) has risen annually at a rate of 5 percent since 2007. The year 2011 stands to mark the fifth consecutive year that such an increase has occurred.
Recently, the steering committee for the KIC and South Korean and North Korean authorities reached an agreement to accept a 5 percent wage hike for North Korean workers at the complex. Accordingly, as of August 1, 2011, North Korean workers at the KIC should earn USD 63.814 rather than USD 60.775 in monthly wages. South Korean authorities, as an exchange for accepting the North Korean demand for a wage increase, requested that productivity be elevated via the adoption of a more efficient method of worker placement.
At the meeting, the Kaesong Industrial District Management Committee, representatives of companies in the complex, and the head of corporations were in attendance and reached an agreement to form a task force specifically for the improvement of productivity of workers. While the overall output of the KIC has increased, the output per worker has not improved, leading to the decision to establish the task force, with the goal of enhancing the competitiveness of the complex.
The minimum monthly income of USD 60.775, which kicked in last August, remained in effect until July 31 of this year. The Labor Law of the KIC caps the wage increase at 5 percent; a 5 percent increase to the minimum wage this year would elevate the minimum monthly wage for workers to USD 63.814.
At the meeting, North Korea mentioned international wage levels and made demands for a wage hike of more than the upper limit. However, most of the companies that operate in the KIC adamantly oppose such demands.
Despite the May 24 sanctions implemented by the South Korean government after the March 2010 sinking of the ROK navy corvette Cheonan, the growth of the KIC has continued. The trade volume has increased by 24.23 percent while the production output has increased by 26.1 percent compared to the same period last year.
Although the eight-year old Kaesong Industrial Complex boasts its competitiveness against other industrial complexes in China and Vietnam, it still has many challenges that must be resolved, including employment flexibility and incentive system.
From the institutional perspective, there are many tax benefits that Kaesong offers that industrial complexes in China and Vietnam do not. For example, the enterprise profit tax in Kaesong is at 14 percent. In contrast, China and Vietnam abolished the preferential treatment for foreign companies in 2008 and 2009, respectively; they currently apply a 25 percent of enterprise profit tax to both domestic and foreign companies. Even in terms of labor and wages, the KIC would appear to offer better quality of labor. In addition, the labor productivity of the KIC is comparable to 71 percent of South Korea, which is much higher than that of China’s Qingdao Industrial Complex (60 percent) and Vietnam’s Tanttueon Industrial Complex (40 percent).
Another advantage is the KIC’s favorable geographical proximity to South Korea, which helps reduce distribution costs and time. This advantage helps to reinforce the sales competiveness of the companies in the complex. In addition, the KIC has sufficient potential for expansion into markets in China, and domestic markets in South and North Korea.
On the other hand, Kaesong has relatively low flexibility of employment due to the principle of indirect recruitment. Difficulties in applying an incentive system are also a disadvantage of the KIC.
ORIGINAL POST (2011-7-15): Kaesong wages set to increase. According to Yonhap:
The minimum wage for workers at the inter-Korean industrial park in the North Korean border town of Kaesong is likely to rise 5 percent this year, the same annual rate of increase since 2007, industry sources said Friday.
More than 46,000 North Koreans work at about 120 South Korean firms operating in the complex, despite the South’s suspension of all other economic ties with the North over the deadly sinking of a South Korean warship last year. The local workers currently earn a minimum monthly income of US$60.775 following a 5 percent increase that took effect last August.
This year’s new minimum rate goes into effect next month after negotiations between the factory park’s management officials from the two sides. Under the park’s labor regulations, the minimum wage can increase only up to 5 percent from the previous year.
“The North Koreans are demanding an increase of more than the upper limit (of 5 percent), citing wage levels in other parts of the world,” said an official from one of the South Korean firms in Kaesong. The person spoke on the condition of anonymity.
“In effect, this is equivalent to demanding a wage rise of 5 percent,” the official said, adding that the businesses operating in the joint industrial park had tentatively agreed to accept the demand. After the increase, the North Korean workers will earn $63.814 monthly.
Meanwhile, production at the industrial zone has continued to grow, according to recent data. The park’s output of clothes, utensils, watches and other goods rose 26.1 percent last year from 2009. Since its opening in 2004 under former liberal South Korean President Roh Moo-hyun, the complex has served as a source of tens of millions of dollars for the cash-strapped North annually.
Read the full story here:
Minimum wage for N. Koreans in Kaesong likely to rise 5 pct
Yonhap
2011-7-15