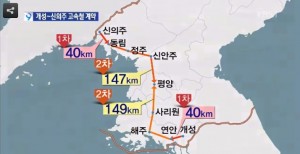
Pictured Above (KBS): A map of the planned high-speed rail project
UPDATE 4 (2014-4-29): The Choson Ilbo reports that Ms. Choi has returned from the DPRK:
The Organisation for Co-Operation between Railways (OSJD) has decided to hold two major meetings, the Commission on Freight Traffic in 2015 and Conference of General Directors in 2019, in Seoul.
KORAIL president Choi Yeon-hye made the announcement at Gimpo Airport on Monday after returning from an OSJD meeting in Pyongyang. It is unprecedented for an associate rather than full member to host the conference.
The OSJD is an organization of 27 former and current communist countries, including Russia, China and North Korea.
“We don’t know yet whether the North will attend the meetings in 2015 and 2019, but the participants unanimously decided to hold them here, and the North didn’t oppose it, so we expect them to come,” she added.
The annual conference of general directors alternatively takes place in Asia and Europe, but exceptionally the 2019 meeting will also be held in Asia following the 2018 meeting in Vietnam.
The government here is keen to work with the railway body to link South Korea to Eurasia via North Korea.
UPDATE 3 (2014-4-22): The Choson Ilbo reports that the head of Korail has left for the DPRK:
KORAIL president Choi Yeon-hye is appropriately on her way to North Korea by train.
Choi left for Pyongyang on a train from Beijing on Monday afternoon to attend a meeting of the Organisation for Co-Operation between Railways (OSJD), KORAIL said Monday.
The OSJD is an organization of 27 former and current communist countries, including Russia, China and North Korea.
The government approved Choi’s request to visit to the North on Sunday after the North sent her a letter of invitation. She got a visa from the North Korean Embassy in Beijing the same day.
The train runs from Beijing to the North Korean border city of Sinuiju in 24 hours, where she switches trains for the 225 km stretch to Pyongyang.
A KORAIL executive said, “Choi’s visit is the North’s first approval of a South Korean official’s visit” since the South imposed sanctions against North Korea in 2010.
She is the first senior South Korean figure to visit Pyongyang since the inter-Korean summit in 2007.
President Park Geun-hye is keen to connect South Korea to Eurasia by railway, which requires cooperation from the OSJD.
UPDATE 2 (2014-4-7): KBS has a report (in Korean) on the project. See the report here. Seoul Village has translated some of the details.
Construction would last 6 years, with two waves that have not been fully detailed yet:
1st stretches: 80 km
From the North: Sinujiu Station – Tongrim Station (Sinujiu-Dongnim, 40 km)
From the South: Kaesong – Yonan (Gaesong-Yeonan, 40 km)
2nd stretches: 296 km
From the North: Tongrim – Chongju – Sinanju – Pyongyang (Dongnim-Jeongju-Sinanju-Pyongyang, 147 km)
From the South: Yonan – Haeju – Sariwon – Pyongyang (Yeonan-Haeju-Sariwon-Pyongyang, 149 km)
UPDATE 1 (2014-4-7): Korail may be involved in the high-speed rail project. According to the Hankyoreh:
News of a recent agreement between North Korea and China to build an international high-speed railroad and highway between Sinuiju (a city on the Chinese border) and Kaesong is raising questions about the fate of a scheduled North Korea visit on Apr. 24 by Korail CEO Choi Yeon-hye.
If Korail does participate in the project, it would bring South Korea one step closer to the Asian continent via the North Korea-China high-speed rail project, which comes on the heels on North Korea‘s Rajin-Hasan development project with Russia.
South Korean businesspeople in China who are closely involved in the high-speed rail project said on Apr. 6 that a contract for the railway/highway construction was signed in Beijing on Feb. 24 by North Korea’s State Economic Development Commission, chaired by Kim Ki-sok, and a Chinese consortium headed by the Shangdi Guanqun investment company. The line would be 376 km in length and connect Sinuiju with Chongju, Sukchon, Pyongyang, Haeju, and Kaesong, with the five-year construction beginning in 2018 with a budget of US$21 billion, or around 22 trillion won. The method would be a Build-Operate-Transfer (BOT) arrangement, with an international North Korean-Chinese consortium providing the investment and delivering the line to North Korea once the costs are recouped. A survey team for the Chinese consortium is reportedly scheduled to visit North Korea in late April.
The chances of South Korea participating are higher in the wake of President Park Geun-hye’s speech in Dresden on Mar. 31. There, she declared that an “organic linkage between South Korean capital and technology and North Korean resources and labor could contribute to building a future economic community on the Korean Peninsula.”
She also said she planned to “achieve shared development for the Korean Peninsula and Northeast Asia both through collaborations with North Korea and Russia, as with the current Rajin-Hasan distribution project, and collaborations with North Korea and China focusing on Sinuiju.”
Further increasing the possibility of South Korean participation are guidelines handed down in January by North Korean leader Kim Jong-un, who said North Korea should work with China and South Korea on an international line through a privately funded BOT arrangement.
Meanwhile, Korail is awaiting Ministry of Unification approval on a request to allow CEO Choi Yeon-hye to travel to North Korea to attend a general directors’ conference for the Organisation for Co-Operation between Railways (OSJD), which is scheduled to take place on Apr. 24.
“Our basic position is to approve visits to North Korea in cases of international events,” said an official from the ministry on condition of anonymity, adding that a final decision would be made “after discussions with the other agencies.”
But Korail remains cautious about the possibility of future cooperation, whatever the outcome for Choi’s visit ends up being. Speaking on condition of anonymity, a source there said, “We’re preparing data on things like a plan to expand cargo transport for different continental rail zones, which is one of the topics on the agenda at the OSJD meeting.”
“We’ve never officially examined the North Korea-China high-speed rail project, and it doesn’t look like it would be economically feasible anyway unless a section is opened between Seoul and Kaesong,” the source added. “Anyway, the government has not decided on participating, and that‘s not a matter that KORAIL can weigh in on by itself.”
ORIGINAL POST (2013-12-20): High Speed Rail and Road Connecting Kaesong-Pyongyang-Sinuiju to be Built
Institute for Far Eastern Studies (IFES)
2013-12-20
On December 8, 2013, North Korea reached an agreement with a consortium of international companies to construct highways and high-speed railroad connecting Kaesong, Pyongyang, and Sinuiju.
The agreement between North Korean authorities and a consortium representing the Chinese companies was signed in both Chinese and Korean by Kim Chol Jin, Vice-Chairman of State Economic Commission of North Korea and representatives from state-owned enterprises of China’s Commerce Department.
The construction period was designated as five years and businesses will operate the rail for 30 years and return the operation rights to North Korean government in the form of a BOT (build-operate-transfer) project, worth a total of 15 trillion KRW. The high-speed rail will be a double-track system with a speed of more than 200km per hour, and the construction of four-lane highway will be built adjacent to the railway. Fence will also be built to prevent unauthorized access to the railway.
The construction zone will cover the areas of Kaesong, Haeju, Sariwon, Pyongyang, Sinanju, Jongju and Sinuiju, approximately 400 km in total length and from Sinuiju will connect to Chinese cities via railway while from Jongju will connect with the Rajin-Sonbong SEZ (special economic zone) to the Russian Khasan railway to be linked with the Eurasian railway.
The consortium working group is planning to visit North Korea to confirm the specific construction plans. It was tentatively decided that the formal contract be signed in Pyongyang based on the proposal submitted by the consortium.
The subject of agreement is a multinational consortium of international investment group, which also includes a South Korean company, which is known as a company involved in North Korean mineral resources development. Once the project is in progress, there are plans of bringing other South Korean companies into the project.
In exchange, businesses will obtain the development rights of extracting gold from Hyesan City (Ryanggang Province) and iron ore in Musan (North Hamgyong Province). North Korean officials are claiming that this project was the legacy of Kim Jong Il and welcomed the participation of South Korean companies.
In March 2011, former North Korean leader Kim Jong Il is reported to have instructed that inter-Korean exchange programs be continued. Upon the completion of the railways and highways, the Presidium of the Supreme People’s Assembly will proclaim international road operations to ensure its stable operation.
The operation rights will be given to the consortium for 30 years while the ownership rights will be shared by the North Korean government and the consortium.
China is also building new railway lines up towards the North Korean border.