By: Benjamin Katzeff Silberstein
Is China enforcing UN sanctions on North Korea? Is “maximum pressure” still on and working? How much is China really trading with North Korea?
None of these questions can really be answered with the open-source information available at the moment. In fact, I doubt that any sources exist that could provide a conclusive answer. Much of the relaxation in Chinese implementation of the various bans and limitations on trade with North Korea likely comes from the Chinese authorities simply turning a blind eye, and how do you record trade that happens because you’re looking away?
The best information we have, unsatisfactory as it may be, comes from anecdotal observations along the border between China and North Korea. Nikkei Asian Review recently visited the border area and gives us an interesting and informative look at what the situation is like in the region. However, the information given through reports such as this one is not enough to jump to the conclusion that China has stopped enforcing sanctions on North Korea. As I explain further below, until we see significant, meaningful amounts of coal and textiles crossing the bridge, North Korea is still suffering immense losses in its export incomes from Chinese implementation of sanctions.
The problem is that this is, of course, hard to see with your own eyes when you visit the border areas. After all, you can’t see what’s not there. To be sure, report such as this one matter a great deal, and I’m not at all discounting its value. The fact that there’s immense, vibrant and dynamic economic activity going on by the Sino-Korean border is interesting in its own right, as it dispels the notion that North Korea is fully isolated economically. As Nikkei shows, that’s just not the case:
The number of trucks making their way across the Sino-Korean Friendship Bridge increased sharply in November, according to an executive of a housing materials supplier in the border city of Dandong.
Many carry plywood flooring, elevator components and other materials to construction projects in North Korea, while seafood heads in the other direction.
I saw similar goods transported over in great quantities in the summer of 2016, another point in time when China was supposed to be squeezing North Korea economically, according to the sanctions frameworks in place.
“These days, the bridge gets jammed with traffic, which is something we rarely saw after the sanctions resolution” in 2017, the executive said.
This is a similar impression to what we’ve seen in other news reports. Traffic declined drastically during the US-North Korea tensions of 2017, and the during the late summer and fall of that year in particular, when round after round of sanctions were levied on the country.
However, that traffic has increased from a relatively extreme low point is itself not evidence that sanctions no longer have any effect. Traffic alone does matter as an indication, but not much more. We need to know what is being shipped as well.
Increased bilateral trade serves both countries’ aims. Beijing wants to strengthen its influence over Pyongyang, while the Kim Jong Un regime needs to develop a struggling economy. Activity at the border area highlights attempts to rebuild ties.
About 70% of China-North Korea trade passes through Dandong. In late November, construction work could be seen getting underway in Sinuiju on the other side of the Yalu River, which separates the two countries.
A large, cylinder-shaped building is taking shape close to the bridge, in an area that also hosts an amusement park. According to local rumors, it is a hotel that will target Chinese tourists.
About 10 km to the south lies the New Yalu River Bridge, which is expected to replace the older crossing as the main cross-border artery when it opens. Many structures that look like new apartment buildings can be seen close to it on the Korean side.
The North Korean leader has shifted his focus to economic policy amid improving relations with China and South Korea.
Sinuiju will potentially be crucial to driving economic growth through trade with China. This past summer, Kim inspected cosmetics and textile plants in the city, and many believe Pyongyang has stepped up the development of nearby areas.
And just a few weeks ago, Kim Jong-un oversaw the Sinuiju grand redevelopment plan.
The sanctions imposed on the Kim regime over its nuclear and missile programs make it difficult for the country to rebuild its economy on its own.
China, which accounts for 90% of North Korea’s total trade in value terms, is backing efforts to revitalize the city.
Black North Korean clams are easily distinguished from the yellow Chinese variety, claimed a middle-aged woman at the Donggang Yellow Sea market as she hooked some out of a net and sorted them by size.
The Chinese authorities toughened controls on imports of clams, crabs and other seafood from North Korea immediately after the sanctions were imposed, but several wholesalers said smuggling in the Yellow Sea had picked up again this past spring.
North Korean seafood at the market, they claimed, was simply being packaged as if it came from China. The clams served at a restaurant in the city were all black.
The sanctions also restrict the acceptance of North Korean workers.
At a garment factory in suburban Dandong, however, there were a number of female laborers from across the border, and what appeared to be a North Korean merchant was seen staying at a luxury hotel in the area, neither of which would have been common sights just after the sanctions were imposed. These people most likely enter China on short-stay permits, rather than working visas.
Guest workers appear to have been one of the first areas in which China began relaxing control, shortly after Kim Jong-un’s spring 2018 visit to Beijing.
Chinese influence in North Korea’s construction sector also appears to extend well beyond the supply of materials.
“It is hard to imagine they have the technology to construct a round building,” said a senior official of a construction materials company in Dandong, speaking about the supposed new hotel on the other side. What is less hard to imagine, he assumed, is where the technical support was coming from.
Locals claim that a Chinese inspection team had gone over to look at the construction of roads linking the new bridge with the nearby town.
Full article and source:
China-North Korea border trade thrives again, despite sanctions
Daisuke Harashima
Nikkei Asian Review
2018-12-06
Again, all of this matters. But the question is just how much it matters when North Korean can’t export nearly the same quantities of coal and minerals to China that it has over the past few years. Some might argue that this trade, too, could simply be hidden and kept off of China’s books. I doubt it. Some, perhaps, but absolutely not all or even most of it, simply given the quantities we’re talking about here. I would think you’d have to do quite a few nighttime runs by ship across the Yalu river to get any meaningful quantities across hidden.
Consider the mere magnitude of the numbers we’re talking about here. I unfortunately don’t have time to dig up the latest data right now, but for a sense of proportion: in July of 2017, China imported only 2.7 million tonnes of coal from North Korea, a downturn of 75 percent. To my knowledge, this number hasn’t climbed significantly since, aside from some outlier months before various sanctions have taken effect, and the like. Chinese imports of North Korean coal account for 42.3 percent of total Chinese imports, according to one figure.
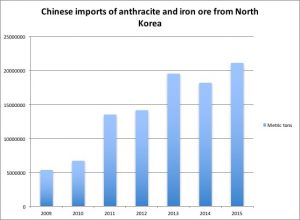
The point isn’t that North Korea is under perfectly applied “maximum pressure” by China. But that trade may be somewhat more porous than a year and a half ago doesn’t mean that North Korea’s economy isn’t experiencing immense difficulties under sanctions at the present moment. I’ll finish this post with a graph showing total volumes of North Korean exports of anthracite and iron ore to China between 2009 and 2015, a period of immense growth in these exports, based on UN Comtrade data. These incomes have been crucial for Kim Jong-un’s ability to orchestrate the massive infrastructure updates and construction projects we’ve seen under his tenure.